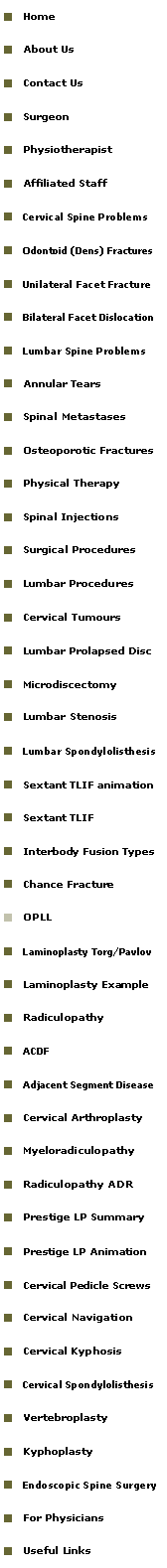
|
Cervical OPLL Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament |
|
· FEATURES · Ossification of ligament that runs behind the vertebral bodies in front of the spinal cord can compress the spinal cord. · Up to 10% of Japanese and Chinese Men over the age of 60 have this condition · Usually asymptomatic, unless patient has severe form or in the presence of congenital canal stenosis |
|
Diagnosed when ossification originates outside the disc within the posterior longitudinal ligament which runs along the posterior aspect of the vertebral body. It is associated with DISH and is classified as an enthesopathy , inflammation of tendon or ligament at the bone-ligament interface. The mechanism of OPLL is similar to that which occurs in DISH with heterotopic bone formation in response to mechanical stress in other tissues. Cartilage cells proliferate first in the periosteum of the vertebral body and then in the annulus fibrosus, longitudinal ligament and dura. The ligament becomes calcified by a process of endochondral ossification. Mature lamellar bone is eventually formed.
Historical It was first described in Guys Hospital Reports in 1838.
Epidemiology Oriental Races especially Japanese have the highest incidence with a prevalence of about 2% in asymptomatic adults. Previously thought rare, it is now found in approx 0.5% of Caucasians, increasing with age. In Japanese men >60 years of age, more than 10% have OPLL. Males to female ratio 2:1 Associated with diabetes. 28% of patients with OPLL have diabetes and 18% are borderline diabetics. The incidence of OPLL in diabetic patients is around 16%. Autoimmune markers HLA BW-40 and SA5 more common in Japanese with OPLL. HLA-B27 which is associated with ankylosing spondylitis is not associated with OPLL.
Most patients with OPLL are asymptomatic. Patients with developmental canal stenosis may be predisposed to earlier symptoms if OPLL is also present. Symptoms are worsened by concurrent cervical spondylosis or infolding or ossified ligamentum flavum. Mild neck sprains may cause syndromes ranging mild numbness to central cord syndrome and occasionally complete tetraplegia.
Treatment is according to symptom severity which may be defined by various scores, the most commonly used is probably the JOA (Japanese Orthopaedic Association) score.
Japanese Orthopedic Association (JOA) scoring system of severity of myelopathy. <7 severe myelopathy 8-12 moderate myelopathy >13 mild myelopathy
Surgery if performed may be either from an anterior approach which usually means a corpectomy and decompression with subsequent strut graft reconstruction. A posterior approach is the other option and this is either laminoplasty or a laminectomy with instrumentation. |
|
Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament |
|
Copyright © 2008 Spine Care Hong Kong |

|
SPINE CARE HONG KONG |
|
ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS, STRUCTURED TREATMENT |


|
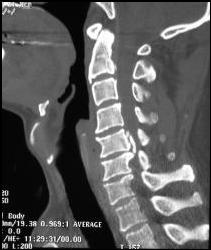
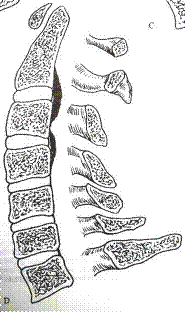
CONTINUOUS |
|
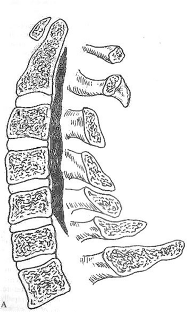
SEGMENTAL |
|
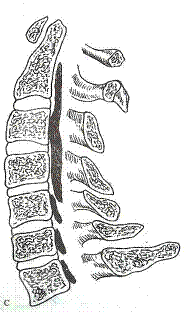
MIXED |
|
LOCALISED |
|
TYPES OF OPLL |
|
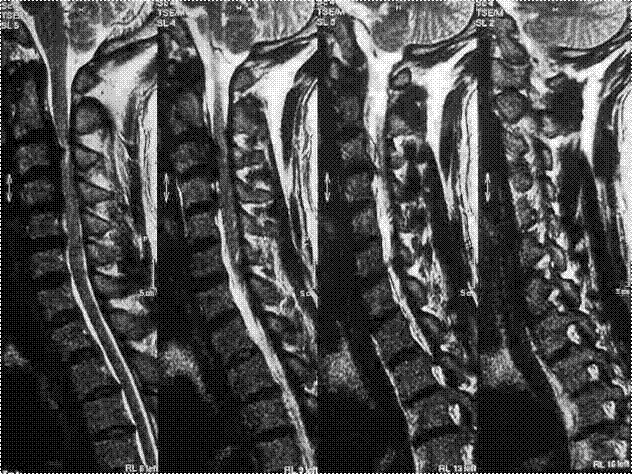
MRI |
|
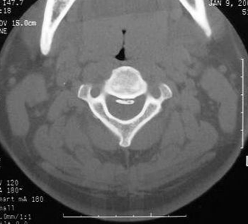
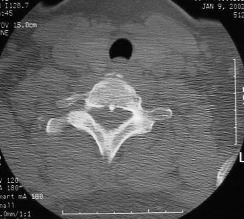
CT SCANS |
|
CASE HISTORY |
|
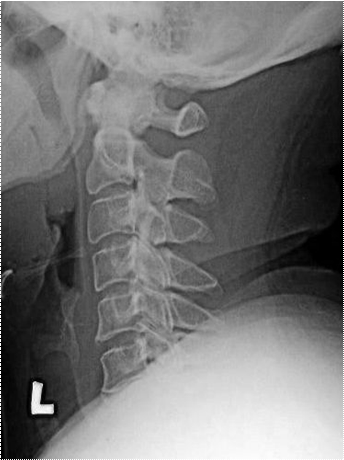
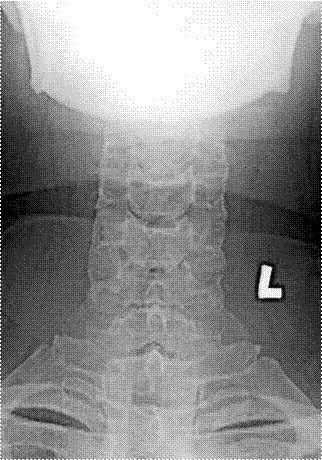
38 year old female History of progressive upper and lower limb numbness Associated with frequent falls, she was having severe difficulty walking Admitted for suspected stroke |
|
RADIOGRAPHS |
|
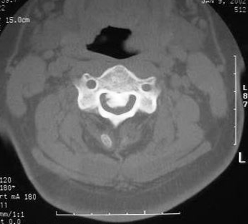
C2 Vertebra |
|
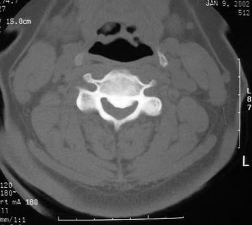
C3 Vertebra |
|
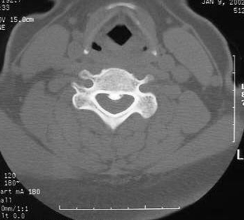
C4 Vertebra |
|
C6 Vertebra |
|
C5 Vertebra |
|
MANAGEMENT AND TREATMENT |
|
Laminoplasty from C2– C7 Progress: Improvement in numbness and weakness of all 4 limbs, walking without the need for any walking aid. |
