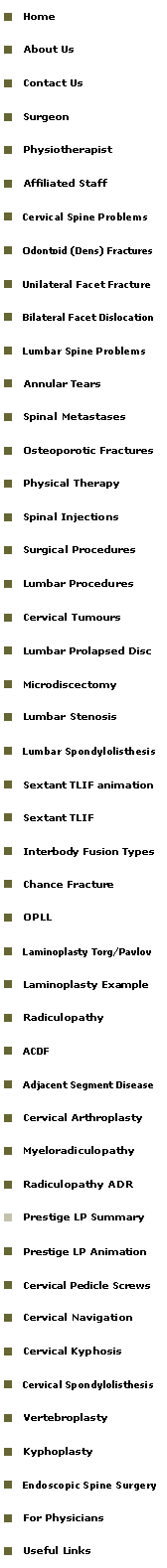
|
Clinical Experience of the First 20 Prestige LP Cervical Arthroplasties |
|
Cervical Disc ARTHROPLASTY with Prestige LP Cervical Disc Replacement
|
|
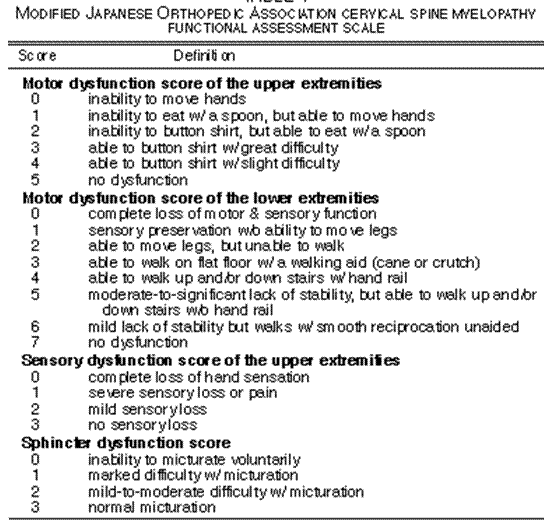
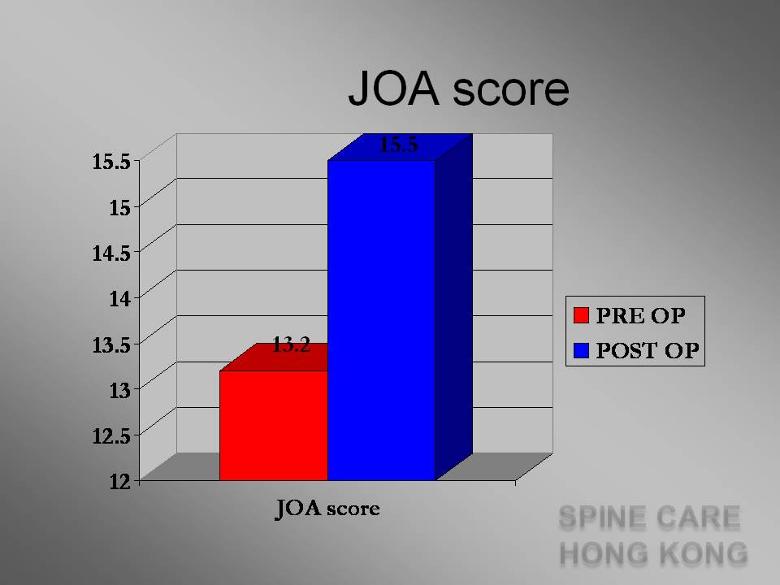
SUMMARY For all 20 patients: neurological symptoms significantly improved |
|
JOA SCORE |
|
NURICK SCORES |
|
SUMMARY DATA
Short term results as regards relief of radicular or myelopathic symptoms comparable to those from ACDF Minimal Subsidence No evidence for H.O. of any evidence of spontaneous fusion in this series Literature up to 9.1% spontaneous fusion
Heterotopic Ossification in Total Cervical Artificial Disc Replacement. Spine. 31(24):2802-2806, November 15, 2006.
COMPARED TO ACDF:
Wider Uncinate Resection Spondylotic Ridge Resection Retention of MOTION may lead to RECURRENCE of Spondylosis as compared to fusion.
Treatment of Radiculopathy with Disc Replacement
Literature Review:
Early Results of a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Comparing Prodisc-C® and ACDF for Cervical Radiculopathy
Conclusion: Treatment of cervical radiculopathy with Prodisc-C® disc replacement and ACDF appears to be equally safe and efficacious at early follow-up. Early range of motion postoperatively appears superior in Prodisc-C® patients.
CSRS 2005 Eric B. Laxer, MD, Daniel B. Murrey, MD, Bruce V. Darden, MD, Alfred L. Rhyne, MD, Alden Milam, MD (Charlotte, NC), Michael E. Janssen, MD, Caroline M. Ponce, BS, Ruth Beckham, NP-C (Thornton, CO)
Artificial Disc versus Fusion for the Treatment of Cervical Radiculopathy: A Prospective, Randomized Study.
Conclusion: The Bryan artificial disc replacement compares very favorably to a conventional anterior cervical fusion for the treatment of patients with cervical radiculopathy.
CSRS 2005 Rick C. Sasso, MD, Robert Hacker, MD (Indianapolis, IN)
Proper Implant Sizing
Overdistraction Increases foraminal height BUT: 1mm overdistraction results in significantly less ROM over FSU (NASS 2006) |
|
Japanese Orthopedic Association (JOA) scoring system of severity of myelopathy. <7 severe myelopathy 8-12 moderate myelopathy >13 mild myelopathy |
|
Nurick Score Grade 0: signs and symptoms of root involvement but without evidence of spinal cord disease. Grade 1: signs of spinal cord disease but no difficulty in walking. Grade 2: slight difficulty in walking but does not prevent full-time employment. Grade 3: severe difficulty in walking that requires assistance and prevents full-time employment and avocation. Grade 4: ability to walk only with assistance or with the aid of a frame. Grade 5: chairbound or bedridden.
Odom’s Criteria Excellent: All preoperative symptoms relieved; abnormal findings improved Good: Minimal persistence of preoperative symptoms; abnormal findings unchanged of improved Fair: Definite relief of some preoperative symptoms; other symptoms unchanged or slightly improved Poor: Symptoms and signs unchanged or exacerbated |
|
ASSESSMENT OF OUTCOMES JOA Myelopathy score Nurick Score Odom’s Criteria |
|
Copyright © 2008 Spine Care Hong Kong |

|
SPINE CARE HONG KONG |
|
ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS, STRUCTURED TREATMENT |

